About Radio Frequency
Sealing / Welding
What is R.F. Heat
Sealing?
R.F.(Radio Frequency)
Heat Sealing/Welding
a.k.a. Dielectric Sealing, Electronic
Sealing/Welding, High Frequency Heat
Sealing/Welding
Brief
Description
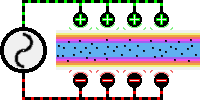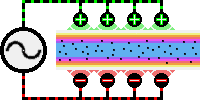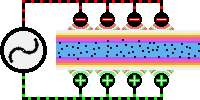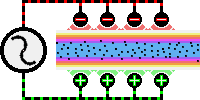
R.F.
heat sealing is accomplished by sending a high frequency
(heating) current through two or more layers of
thermoplastic material placed between two sealing electrodes
or dies. One die is shaped in the image of the required
seal. The other die may have the same shape or may be a flat
plate. The dies are usually mounted on a pneumatic or
hydraulic press to provide pressure for fusing the
materials. The high frequency energy produces localized
heating by exciting the molecules of the materials to 27.12
MHz , causing them to melt, thus allowing their molecules to
intermingle, where upon the pressure exerted on the material
brings about a thorough fusion. The current is then shut
off, the material is allowed to solidify during a brief
cooling period, the materials become joined together at the
point of the seal. The resulting seal can be stronger than
the original workpiece materials.
General
Considerations
The Quality of a
seal is determined by three factors:
1.
Sealing Current ( R.F. Power
)
2. Sealing time
3. Pressure
To
some extent these three factors are independent of one another:
for example, more current or more pressure does not necessarily
reduce the sealing time. The type and thickness of the material
and the total area of the seal determine these factors.
Pre Seal time and a heated platen can also change these
factors
View:
Material Sealability
Chart
Sealing Area
Chart
Glossary of
Terms
Learn more About
:
Arcing
& Arc
Suppression
Buffers
|